DH for various processes:
The enthalpy of formation of a compound,
is the enthalpy change when one mole of compound is formed under standard
conditions from one mole of its constituent elements in their standard
state.
e.g.
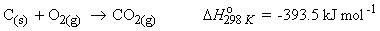

=>
The enthalpy of combustion
(or the heat of combustion) is the enthalpy change when one mole of compound
reacts completely with excess oxygen under standard conditions.
e.g.
The bond dissociation enthalpy (bond energy) represents the energy required to break one mole of chemical bonds in the gas phase. The term 'mean bond dissociation energy' is more commonly used, since the actual energy required to break a particular bond is dependent on the precise environment of the bond.
Consider the dissociation of methane by successive breakage of C-H bonds:
We have:
(i)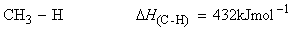
(ii)
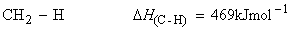
(iii)
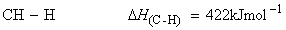
(iv)
Given this information we may estimate the mean bond dissociation
enthalpy for C-H given by:
The 'phase change' enthalpy represents the energy required/given off when one mole of pure substance changes phase. Note:
(1) DH(freezing) = - DH(fusion), etc.These are usually quoted under 1Bar pressure, at the temperature where the phase change occurs.
(2) DH(sublimation) = DH(fusion) + DH(vaporisation)
(5) Enthalpy of Solution.
The enthalpy of solution is the enthalpy associated with the process when a process enters solution. There can be different types of enthalpy of solution, the most common being:
(a) The integral enthalpy of solution - the enthalpy change when one
mole of solute dissolves in a large excess of pure solvent.
e.g. HCl(g) + (aq) -> HCl(aq) DH = 74.4kJ mol-1
(b) The differential enthalpy of solution - the enthalpy change
when one mole of solute dissolves in a large amount of solution.
e.g. DH for dissolving 1 mole of HCl(g) in 0.1M HCl is different from DH for dissolving 1 mole of HCl(g) in 1M HCl, and is different from the 74.4 kJ mol-1 quoted above.
(c) The enthalpy of hydration is reserved for the special case when
the solvent is water.