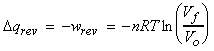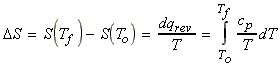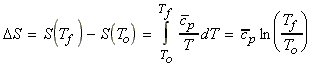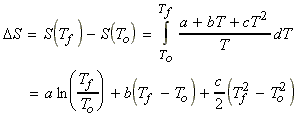A quantitative measures of
DS and the effect
of T on DS
- A quantitative measures of DS:
- Entropy changes during the phase change - Trouton's rule
- Changes in entropy during isothermal expansions of an ideal gas,
- Changes in entropy during the heating of an ideal gas,
- The effect of T on DS
(1) Entropy changes during the phase change - Trouton's rule
At constant pressure (standard conditions),
i.e.
For example:
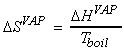 |
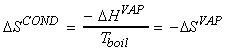 |
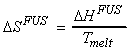 |
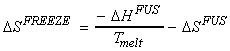 |
|
+ve entropy = more disorder |
-ve entropy = less disorder |
Trouton's rule:
Trouton's rule states that most liquids have approximately the same value for the entropy of vaporisation as illustrated in the table below (about 85 J K-1 mol-1). Exceptions may be due to:
(i) Liquids where the molecules have an 'extra' amount of order in them, due for example, hydrogen bonding (e.g. water). In such cases, the DS is larger than the typical 85 J K-1 mol-1 for systems having the 'normal' amount of disorder in the liquid phase.
(ii) Very light molecules (e.g. methane) are difficult to excite to rotation. This means that the gas phase has 'less' disorder then in 'normal' cases. In such cases, the DS is lower than the typical 85 J K-1 mol-1 for systems having the 'normal' amount of disorder in the gas phase.
(kJ mol-1) |
Boiling point
(oC) |
(J K-1 mol-1) |
|
| Benzene | +30.8 | 80.1 | +87.2 |
| carbon tetrachloride | +30. 0 | 76.7 | +85.8 |
| cyclohexane | +30.1 | 80.7 | +85.1 |
| hydrogen sulphide | +18.7 | -60.4 | +87.9 |
| Methane | +8.18 | -161.5 | +73.2 |
| Water | +40.7 | 100.0 | +109.1 |
(2) Isothermal expansion of an ideal gas
For an siothermal process, DU = 0, i.e.:
Thus:
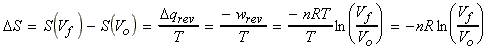
or:
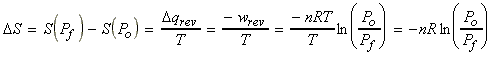
(3) Changes in entropy during the heating of an ideal gas - effects of temperature on entropy.
When we heat an ideal gas we have:
i.e.:
(a) Assuming that over the range (To,Tf) cp is constant, we have:
(b) Assuming that over the range (To,Tf)
cp
may be estimated through a quadratic: