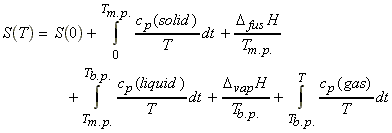The third law of thermodynamics (Nerst
heat theorem) and absolute entropies
The third law of thermodynamics (Nerst heat theorem) staes that the energy of a perfect crystal at 0K is 0.
Note - This perfection can never be reached (e.g. isotopes, different
nuclear spins) and gives rise to the so called residual entropy.
Standard/Absolute entropies
Def'n: The standard entropy
of a compound is the molar entropy at 298.15K and 1 Bar pressure.
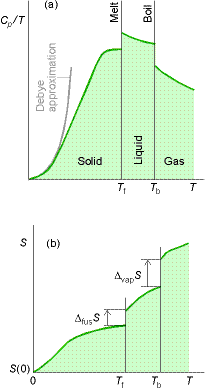
The entropy at a temperature T (and 1 Bar pressure) is calculated as follows (see figure below) :
(1) All the properties (except S(0) can be measured experimentally. Note that if we assume that S(0) = 0, then the entropy takes the name of absolute (or third law) entropy.
(2) The integrals can be either calculated graphically from the curve 'cp/T' vs. 'T' (see fig. below), by fitting a polynomial and then integrating the polynomial analytically, or by evaluating the area of a plot of cp vs ln(T).
(3) T here is a problem in evaluating the integral:
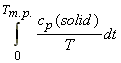
since it is difficult to evaluate cp in the limit
of 0K. We hence make use of the Debye extrapolation, i.e.
(a) measure cp to as low a temperature as possible;(b) fit a curve of cp = aT3 to the data collected, and determine the value of 'a';
(c) Assume that the expression cp = aT3 remains valid up to T = 0K.