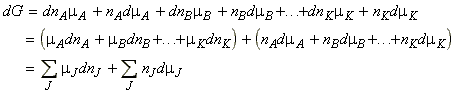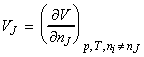5. Chemical potential, simple mixtures, chemical reactions andequilibria
(ii) Mixtures
The Gibbs-Duhem equation
Since the total free energy of a system is give by:
and hence by differentiation we get:
But, as discussed in the previous section, for a system at constant temperature and pressure we have:
and hence since G is a state function, then the two expressions must be equal, which means that:
The significance of the Gibbs-Duhem equation is that the chemical potential of a component in a mixture cannot change independently of the chemical potential of the other components. For example, in a binary mixture we have:………………….(Gibbs-Duhem equation)
i.e., if one chemical potential increases, the other must decrease.
Note: There is also the a similar 'Gibbs-Duhem equation for the partial molar volumes' which is given by:
where the partial molar volume, defined as:
which signifies the volume of component J in a mixture.