Aims and Objectives
Preventing Deadlock (by denying one of the conditions)
Deadlock Detection
Recovering from Deadlock
Deadlock Avoidance
Not desirable to deny - we want dedicated resources
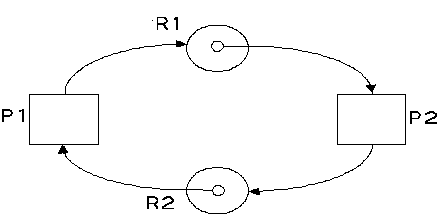
Force processes to request and gain all their resources in one go.
Disadvantages are other processes are made to wait.
A resource which will not be used until the end of a process still has to be requested at the beginning - poor resource utilisation
Some non-shareable resources can be pre-empted if the hardware/software saves the context of the interrupted process - but what about printers?
Only partial denial of no pre-emption is possible.
Resources are grouped into `Frequency of Use' classes, C1, C2, C3, etc.
All required resources belonging to the same class are requested at the same time in class order
No circular wait because either all required resources one class are held, or process waits until all required resources within a class are available.
Disadvantages are that resources must be requested in an artifical order - not necessarily the order in which they will be used.

Abort all deadlocked processes
Restart all deadlocked processes from a checkpoint
Abort processes one at a time
Pre-empt resources from processes
Example, using 12 tape decks
Current Maximum
Loan Need
Process(1) 1 4
Process(2) 4 6
Process(3) 5 8
Available 2
Case A
Process(2) requests and obtains 2 remaining decks. Process(2) can run to completion, releasing all 6 decks providing sufficient resources for the other processes to complete - safe state
Case B
Process(1) requests one deck. State unsafe because there are not enough resources to guarantee completion of all processes - request denied.