|
|
Animal-related
Injuries relevant to the Maltese Islands - Marine
Pisces - inedible
species
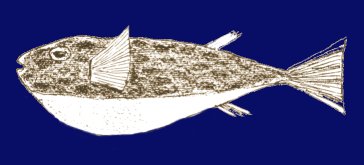 Some fish species must be considered unpalatable or
non-comestible. The main culprit in Malta is the Mediterranean Puffer
Fish Legocephalus legocephalus.
The toxin of the Puffer Fish can be very potent causing a mortality
rate as high as 50% depending on the physical condition of the
individual, and the amount of fish eaten. The poison present in the
flesh or viscera of the fish apparently exerts its primary effect on
the peripheral nervous system, but the physiologic mechanism is as yet
unknown. The toxicity is dependant on the feeding pattern of the fish. Some fish species must be considered unpalatable or
non-comestible. The main culprit in Malta is the Mediterranean Puffer
Fish Legocephalus legocephalus.
The toxin of the Puffer Fish can be very potent causing a mortality
rate as high as 50% depending on the physical condition of the
individual, and the amount of fish eaten. The poison present in the
flesh or viscera of the fish apparently exerts its primary effect on
the peripheral nervous system, but the physiologic mechanism is as yet
unknown. The toxicity is dependant on the feeding pattern of the fish.
 While the Puffer Fish is poisonous during most of the
year, other species such as the Moray Eel Muraena helena are poisonous only
during a part of the year. This snake-like fish has blood which when
fresh is toxic to both humans and animals. Poisoning can occur even
during handling of an injured animal in the presence of cuts on the
hands. When cooked to a temperature of 75C, the toxin looses its
poisonous properties and the fish becomes safe to be eaten. Its bite
can also produce toxic manifestations. Coma and death can occur in
about 12% of cases. While the Puffer Fish is poisonous during most of the
year, other species such as the Moray Eel Muraena helena are poisonous only
during a part of the year. This snake-like fish has blood which when
fresh is toxic to both humans and animals. Poisoning can occur even
during handling of an injured animal in the presence of cuts on the
hands. When cooked to a temperature of 75C, the toxin looses its
poisonous properties and the fish becomes safe to be eaten. Its bite
can also produce toxic manifestations. Coma and death can occur in
about 12% of cases.
Fish normally
considered edible [e.g. grouper, pompano, barracuda, mackerel,
butterfly fish, snapper, sea bass, perch, wrasse, etc.] can become
sporadically poisonous giving rise to fish poisoning manifestations
known as: -
Ciguatera
fish poisoning.
- Symptoms
of acute poisoning begin 30 minutes to 4 hours after ingestion.
- They
include numbness and tingling of the face and lips which spreads to the
fingers and toes.
- This is
followed by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, malaise, dizziness, abdominal
pain, and muscular weakness.
- In severe
cases, the symptoms can progress to foaming at the mouth, muscular
paralysis, dyspnoea, or convulsions. Death may occur from convulsions
or respiratory arrest within 1-24 hours.
- After
recovery from the immediate symptoms, muscular weakness and
paresthesias of the face, lips, and mouth may persist for weeks.
Typically, these paresthesias consist of reversed temperature
sensations - i.e. cold food cause a searing pain, while hot food feels
cold.
Another type of fish
poisoning is that caused after consumption of improperly prepared tuna
and other scombroidei from the growth of surface organisms in fish
stored at ambient temperatures. This type of poisoning is referred to
as:-
Scombroid fish poisoning.
- Some of
the toxic effects may be the result of the release of histamine-like
amines during bacterial decomposition.
- Symptoms
of include nausea, vomiting, cramps, diarrhea, facial flushing,
headache, and burning in the mouth.
- Treatment
of both Ciguatera and Scombroid fish poisoning is symptomatic.
- Remove the
ingested fish by gastric lavage or emesis
- Maintain
an adequate airway and treat respiratory failure
- Manage
convulsions and treat for shock.
- Antihistaminics
have been reported useful to relieve some of the symptoms of Scombroid
fish poisoning.
|






 Some fish species must be considered unpalatable or
non-comestible. The main culprit in Malta is the Mediterranean Puffer
Fish
Some fish species must be considered unpalatable or
non-comestible. The main culprit in Malta is the Mediterranean Puffer
Fish  While the Puffer Fish is poisonous during most of the
year, other species such as the Moray Eel
While the Puffer Fish is poisonous during most of the
year, other species such as the Moray Eel 